Works
Brain Win!
Developing and evaluating a mobile game of cognitive training for elders
Portfolio
Brain Win! A cognitive training game.
The number of elderly people in the world is increasing rapidly. To cope with aging populations, governments and institutions around the world such as WHO have proposed various guidelines. The purpose of these guidelines is generally to propose how elderly people’s cognition ccan be maintained and to encourage their social participation. In this project, the team and I designed a user-friendly cognitive training game for elderly people, which based on their demands and living contexts.
My Role
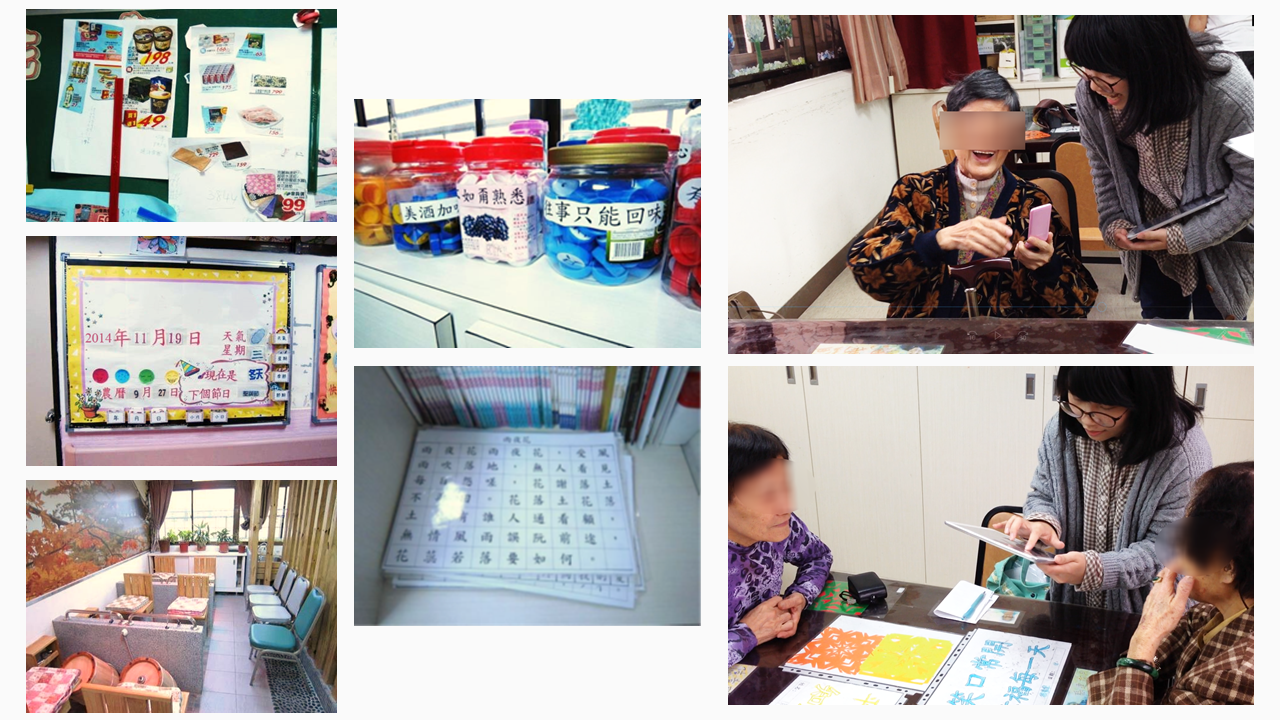
Contextual inquiry
I conducted interviews with older adults and field experts in a daily-care nursing
home to explore their demands and preferences of mobile-based games. Meanwhile, I
investigated the cognitive training activities in the daily care institution.
The findings helped to design the game with familiar content for older adults which
is good for their cognitive processing.
Structure definition
I systematically reviewed theories of age-related cognitive impairments and mobile games. I integrated the results of the contextual inquiry and the literature review to propose the content structure of the game. This helped to construct a reliable and scientific foundation for the game design.
Prototype evaluation
I planned the prototype evaluations and I conducted them in older adults’ homes. I analyzed the results which were used to validate the acceptance of the game and refine the design of it.
Result publication
I planned the prototype evaluations and I conducted them in older adults’ homes. I analyzed the results which were used to validate the acceptance of the game and refine the design of it.
The Challenge
Although previous studies and projects on digital games have provided valuable insight into cognitive training and also suggested design principles for the content and interactions, they have:
- Not frequently used multiple sources (such as stakeholder attitudes and qualitative and quantitative sources) for analysis.
- Not considered older adults’ daily experiences and not applied them in game design.
- Seldom tested games in a realistic context such as homes and nursing homes.
In sum, our goal for the project was to design a high acceptance and user-friendly mobile game of cognitive training for older adults according to their lives and demands. Specifically, our high-level goals were to:
- Determine what types of cognitive training do elderly people accept in a mobile game.
- Identify what components are crucial to improving or reducing the usability of a cognitive training game for elderly people.
The Approach
Design-based research
To address the need to clarify how older users’ cognitive functions can be enhanced by game training in a genuine context with stakeholders, this study adopted the research method framework of design-based research (DBR) to investigate the complex phenomenon. The features of DBR includes that:<
- DBR focuses on the development of hypotheses and a framework and the contribution to model formulation, rather than model estimation or validation.
- DBR typically triangulates multiple sources and types of data to connect intended and unintended outcomes of processes of enactment, and it increases the validity of findings through its typical partnerships and iteration.
- DBR enables researchers to grasp problems through iterative development and places emphasis on the authenticity of the context.
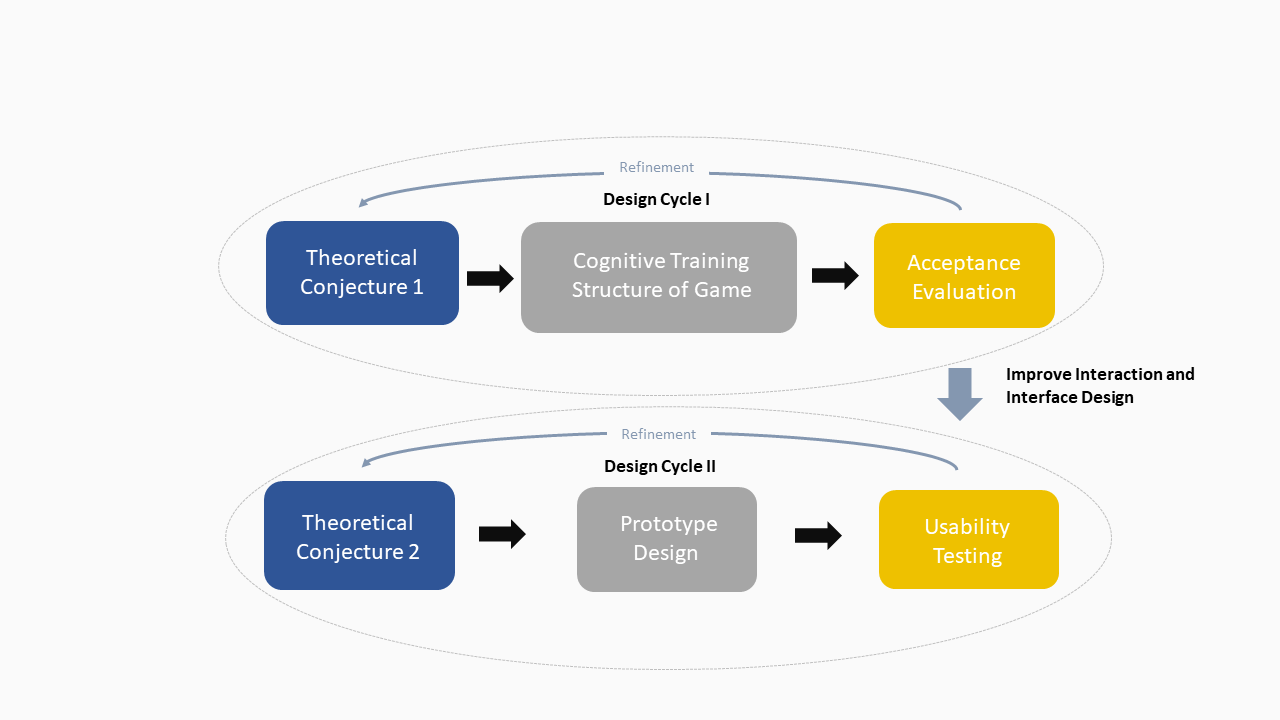
The Discovery
The structure of cognitive training
In line with cognitive theories and product analysis, I proposed aging cognition and cognitive training structure of related games. This structure provided a scientific base for the design of the mobile game in this project.
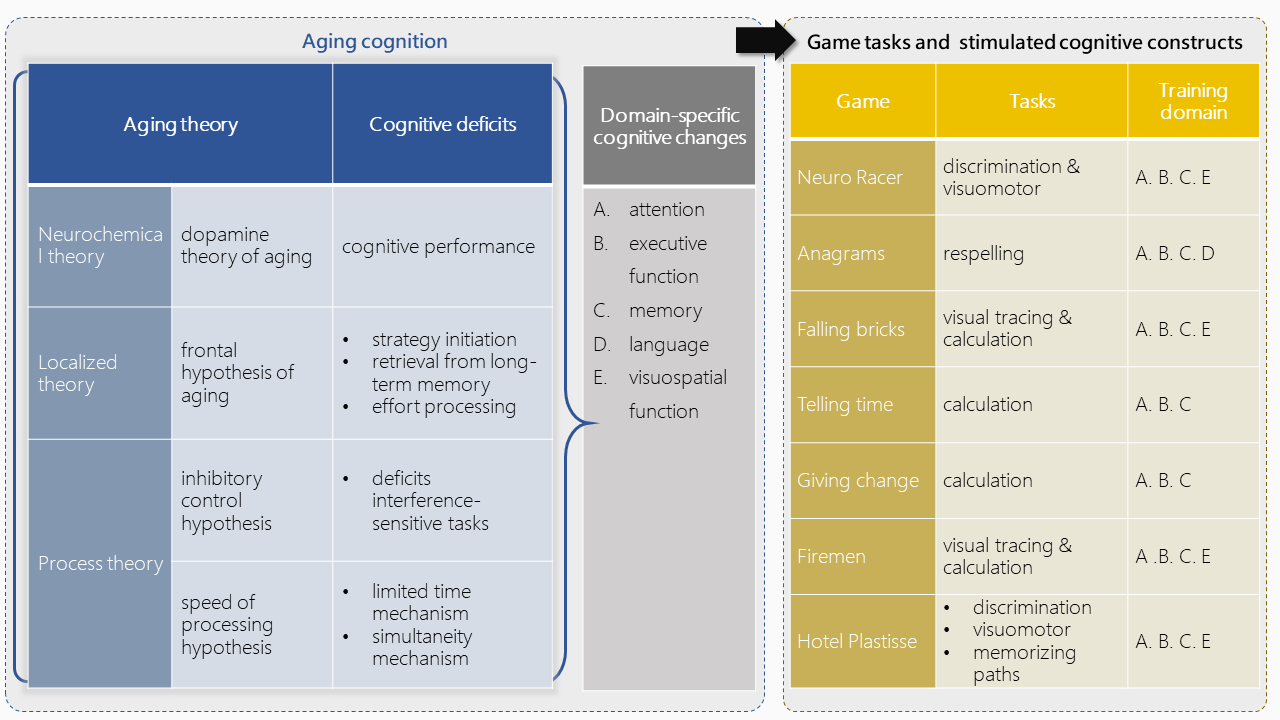
The contents of the game
To design appropriate game tasks for cognitive training, we visited the local day-care nursing home and interviewed a professional manager of it. I analyzed the data and proposed the matrix of cognitive training activities and effectiveness in the day-care nursing home. This result helped to design the tasks in the game.


The Vision
The winner of life–Daily game
Whilst our competitors focus on creating a virtual context (car race, hotel management, firemen, etc.) in games to train older adults’ cognition, our vision was to use familiar components to help users connect their capability between the virtual and the real world. Therefore, we expected that the users can train their cognition, then resulting in a better daily life. We proposed a few specific principles to reach the vision.

The Framework
The framework of game was defined according to the findings in Cycle I. The tasks corresponded to different types of domain-specific cognitive training were proposed.

Prototype
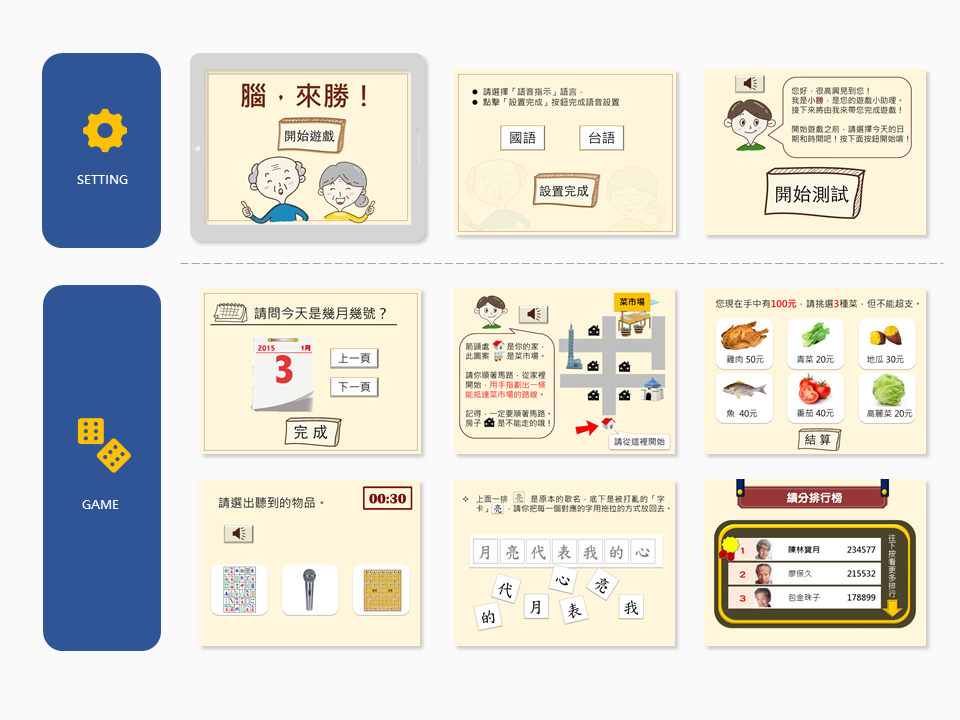
My calendar
Participants had to identify the date by turning the calendar and selecting the correct day and time.
Go to market and shopping
The game specified that the participants wanted to prepare dinner for their grandson’s birthday and had to go to the market to purchase ingredients. The participants had to read the map and draw the route to the market. Afterwards, the participants had to buy three ingredients with a budget of NT$100. During this task, the participants had to concentrate on the information icons and remember the costs of their selected items to perform cumulative calculations.
Finding object during a phone call
In this game context, the participants received a phone call from their son asking them to find something in his bedroom. Participants had to listen for the target word and select the corresponding icon. The auditory cue trained participants to search their semantic memory and retrieve the corresponding icon.
Super singer
In this context, the participants went to karaoke with a friend and had to reorganize the character cards containing song lyrics. The true lyrics were presented, and participants had to move the character cards onto them.
Go to the zoo
In this game, the participants went to the zoo with their grandsons and had to introduce animals to the grandsons after two animals made characteristic noises. Participants had to remember the noises and select the corresponding animals.
Go to the zoo
In this game, the participants went to the zoo with their grandsons and had to introduce animals to the grandsons after two animals made characteristic noises. Participants had to remember the noises and select the corresponding animals.
Once each task was completed, a feedback page indicating success and failure was displayed with applause sounds and encouragement, respectively. When participants successfully completed tasks, they could choose to practice the particular game, check their game scores or check their positions in the ranking table.
Evaluation
Acceptance evaluation
In the first cycle, I used competitors’ cognitive training apps which corresponded to the structure of cognitive training but were lack of content design to evaluate target users’ attitudes toward them. I also observed the interactions between users and the interface of the apps. The evaluation was in the local day-care nursing home.

Usability testing
In the second cycle, I applied hierarchical task analysis (HTA), NASA Task Load Index (NASA-TLX), and follow-up interviews as methods to collect quantitative and qualitative data. The tsets were conductred in older adults' homes.
Refined Design
According to the results, the contexts and tasks of the game were generally satisfying and acceptable. Interface and interaction problems were encountered by users for the My calendar and Shopping in the market tasks, so these were modified.
Improving interface affordance
The mode of calendar turning was changed from button tapping to swiping, which is more intuitive, and this mode was indicated by the textual instruction and a flashing arrow.
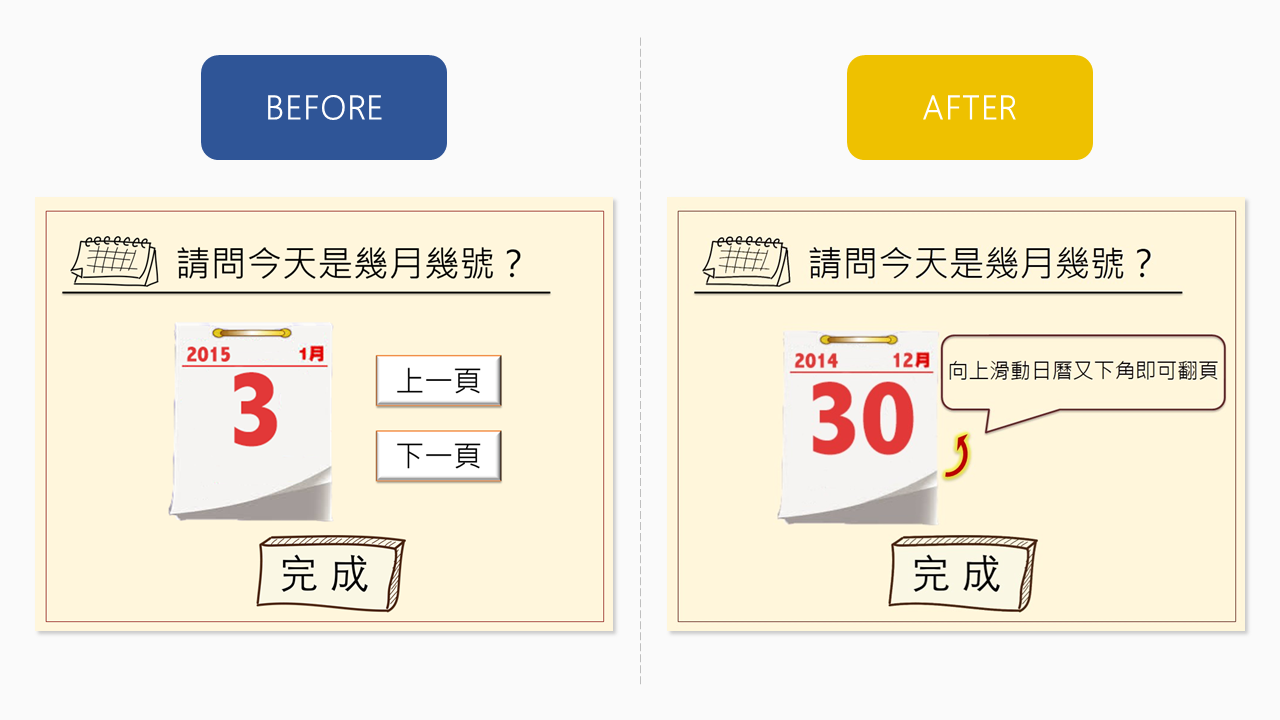
Directing attention
The count button in Shopping in the market was modified to flash with a yellow light to attract the user’s attention after he or she had chosen three ingredients.

Impact
Proposing a useful structure of designing cognitive training game
The outcome of the literature review is the aging cognition and cognitive training structure of related games. Designers can use this structure to design cognitive training games with a scientific base in the future. Meanwhile, this project presented a practical case of using the structure.
International impact
The project was published in the Journal of Frontiers in Psychology with a high
impact factor (SSCI, IF=2.321; 5-year IF= 2.820; 39/135 Psychology). People who
are interested in design, cognitive science, and gerontechnology fields can
refer to this paper by open access.
More than 5,000
readers have viewed the
paper and over 600 readers have downloaded it. This article has more
views
than 78% of all Frontiers articles.
